
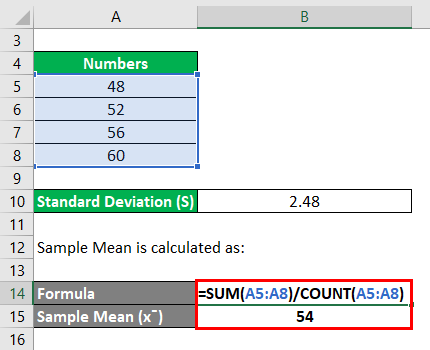
STDEV – STDEV.S was introduced in Excel 2010.Text and FALSE are taken as 0 and TRUE is taken as 1. STDEVA – Use this when you want to include text and logical values in the calculation (along with numbers).STDEV.S – Use this when your data is numeric.Now let’s understand these three formulas: this narrows down the number of formulas to three (STDEV.S, STDEVA, and STDEV function) You can read a great explanation of it here (read the first response).
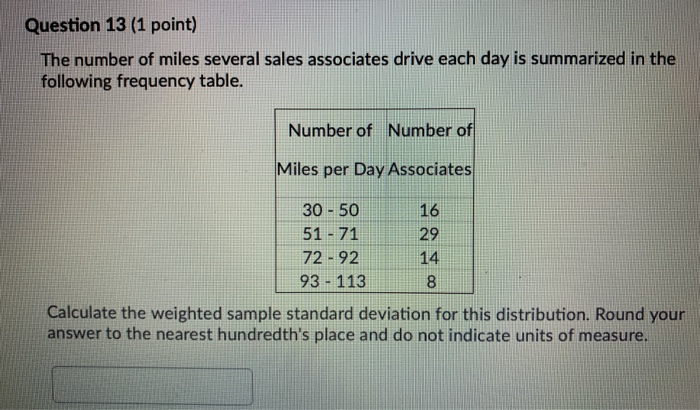
You can use the sample data to calculate the standard deviation and infer for the entire population. In such a case, you pick a sample from the population.

On the other hand, you use term ‘sample’ when using a population is not possible (or it’s unrealistic to do so). In almost all of the cases, you will use standard deviation for a sample.Īgain in layman terms, you use the term ‘population’ when you want to consider all the datasets in the entire population.
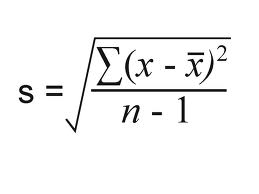
The market cap-weighted benchmark return is calculated asīenchmark return \(= \sum _ \). Th e stock weights and benchmarks returns for a measurement period are given in the graphs below: Stock C and D have market caps of 10% and 5% respectively of the total market. Stock A and Stock B have market caps equal to 45% and 35% respectively of the market’s total capitalisation. We consider a simplified stock market which consists of two large-capitalisations (cap) and two small-cap stocks. The analysis is also applicable when we compare managers against their peers. However, as preparation, we first consider market dispersion from a stock perspective.Īs before, performance is measured against the unbiased market-capitalisation (market-cap) weighted benchmark. If we want to examine how market dispersion affects manager outperformance we have to measure the dispersion of active portfolio returns instead. This measure describes the dispersion in individual stock returns. Here we explain the methodology for calculating an asset-weighted standard deviation of share returns, often also referred to as the cross-sectional standard deviation. Opportunities for successful security selection abounds when market dispersion is high, as discussed before. Market dispersion refers to the variation in returns of the market’s underlying securities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
